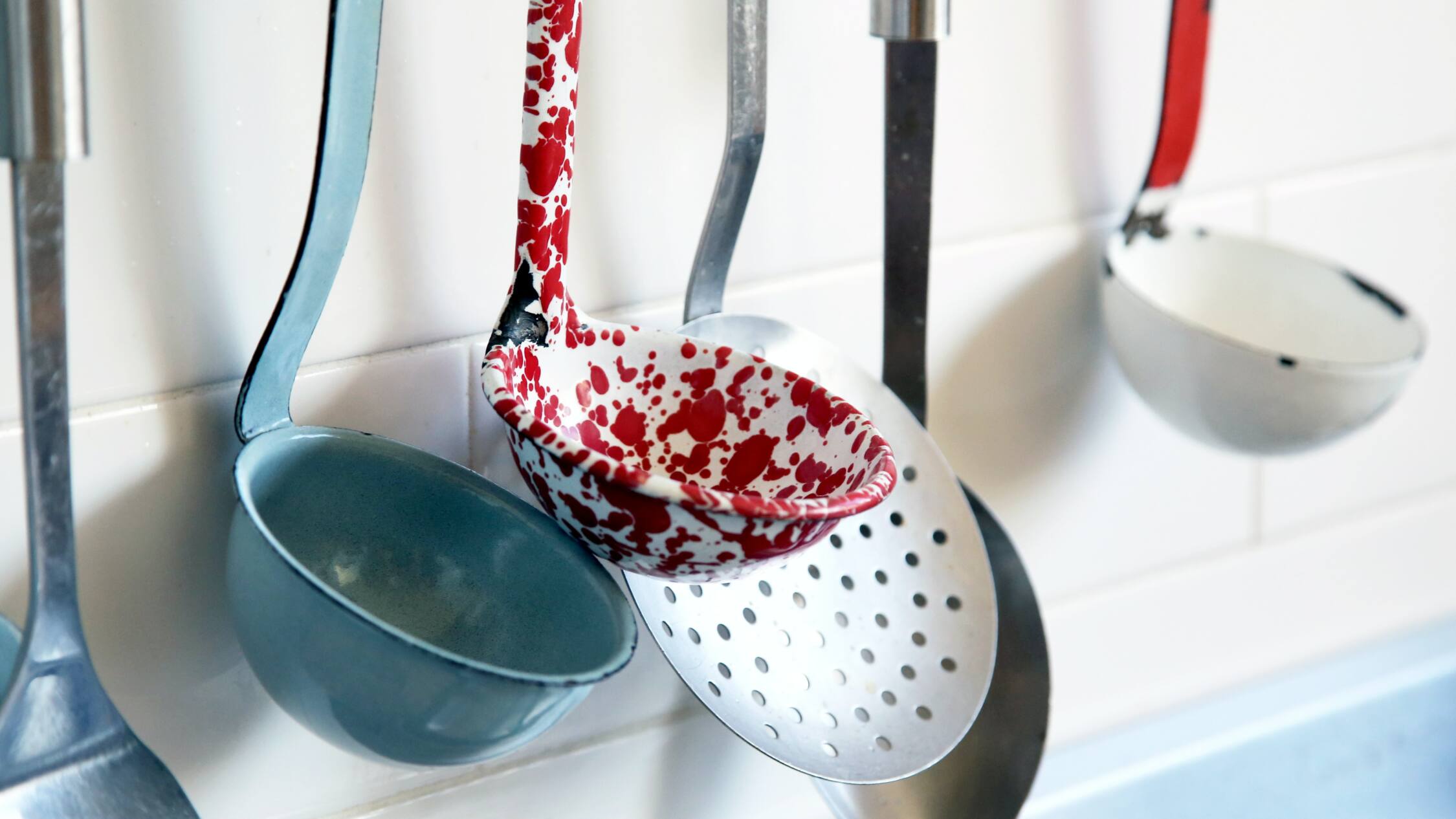
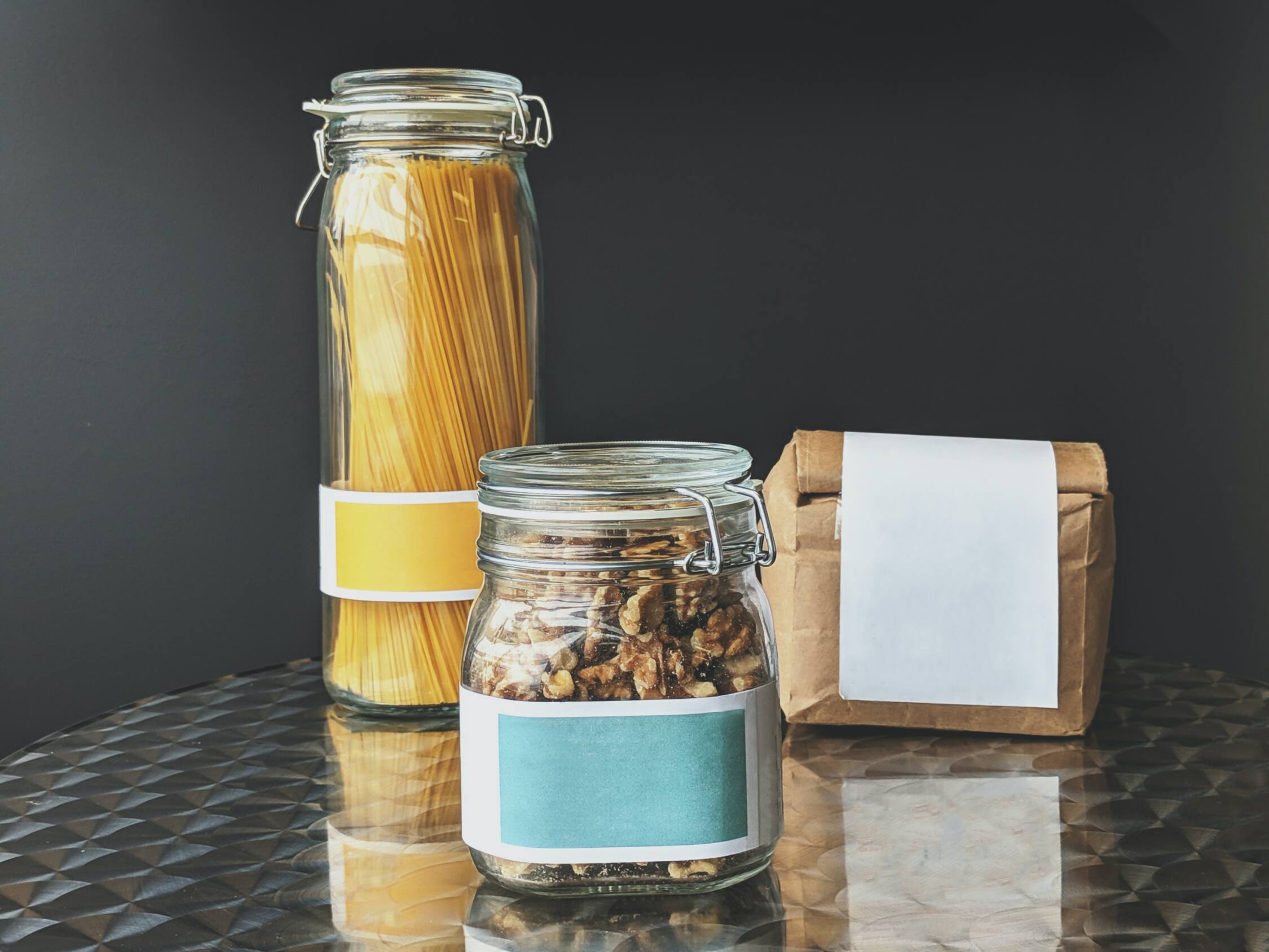
Food Contact Materials (FCMs) are materials intended to come into contact with food, including packaging, utensils, and equipment used in food production and transportation. FCMs can include cutlery, Tupperware, to-go containers, dishes, commercial packaging, and cooking utensils. The safety of FCMs is paramount, as harmful substances may migrate from the materials to the food.
This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of FCM testing, including the applicable regulations and standards, testing methods, test conditions, and regional regulatory requirements.
Have specific questions or want to start testing your product? Contact ACT LAB today to learn more about Food Contact Materials testing.
What are Food Contact Materials?
Food contact materials (FCMs) are substances or materials that come into direct or indirect contact with food during its production, processing, storage, preparation, or serving. These materials are used in various forms, such as packaging, containers, utensils, coatings, and processing equipment. The purpose of food contact materials is to protect and preserve the food, prevent contamination, and ensure food safety and quality.
Examples of common food contact materials include:
- Food Packaging: This category includes materials like plastic films, paperboard cartons, metal cans, and glass bottles used to store and protect food products.
- Food Containers: These are materials used to hold or serve food, such as plastic or glass containers, aluminum foil, and disposable plates or bowls.
- Utensils: Cutlery, kitchen tools, and other utensils made from materials like stainless steel, plastic, or wood that come in contact with food during preparation or serving.
- Food Processing Equipment: Machinery and equipment used in food processing facilities, made from materials like stainless steel, silicone, or food-grade plastics.
- Food Coatings: Substances used to coat or line food contact surfaces, like non-stick coatings on cookware or wax coatings on certain fruits and vegetables.
- Food Wrapping: Materials used directly on the food to protect it, such as plastic wrap or parchment paper.
It’s essential for food contact materials to be safe and not introduce harmful substances into the food they come into contact with. Many countries have regulations and guidelines in place to ensure that food contact materials meet specific safety standards. These standards often dictate the types of materials that can be used, as well as the conditions under which they can be safely employed in contact with food. This helps to minimize the risk of potential chemical migration from the materials to the food and to protect public health.
Food Contact Material Regulations
Regulations related to food contact materials vary from country to country and are often designed to ensure the safety and suitability of these materials for contact with food. Here are some examples of key regulations and guidelines from different regions:
United States:
Food and Drug Administration (FDA):
- In the United States, food contact materials are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
- The FDA sets standards for the safe use of materials like plastics, adhesives, coatings, and paper in contact with food through specific regulations, such as 21 CFR 170-199.
- The agency evaluates the safety of food contact substances and establishes the conditions under which these materials are considered safe for use with food.
European Union:
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA):
- In the European Union (EU), the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) provides scientific advice on food contact materials and substances intended for use in them.
- Based on EFSA’s scientific opinions, the European Commission sets specific regulations for food contact materials.
- The Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 lays down the general principles and requirements for food contact materials.
- There are also specific regulations for certain materials, such as plastics (EU 10/2011) and recycled plastic materials (EU 282/2008).
It’s important to note that both the United States and the European Union have strict regulations in place to ensure the safety and suitability of food contact materials. These regulations aim to minimize the risk of chemical migration from the materials into the food and to protect public health. Manufacturers and importers of food contact materials in these regions must comply with these regulations to ensure their products meet the required safety standards.
How Are Food Contact Materials Tested?
Food contact materials are tested through various methods to ensure their safety and compliance with relevant regulations. The testing process may differ depending on the type of material, the intended use, and the specific regulations in each region. Some typical test procedures for food contact materials include:
- Migration Testing: One of the primary concerns with food contact materials is the potential for chemical substances to migrate from the material into the food. Migration testing assesses the quantity of substances that could transfer from the material to the food and helps determine if the levels are within acceptable limits. Different conditions, such as temperature and time, may be simulated during migration testing to mimic real-life usage scenarios.
- Analytical Testing: Analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry, and other advanced methods are employed to detect and quantify specific chemical substances in food contact materials. These tests help identify any harmful or restricted substances present in the materials.
- Extractability Testing: This type of testing evaluates the potential for the material to release chemical compounds into food when in contact with different food simulants (substances that mimic the properties of different food types). Extractability tests help assess how the material interacts with specific food types and determine potential risks.
- Sensory Testing: Sensory evaluations involve human testing panels to assess any off-flavors or odors that might be imparted to the food due to the contact material. This is particularly important for packaging and sealing materials that might affect the food’s taste or smell.
- Physical and Mechanical Testing: Physical and mechanical properties of food contact materials are also tested. For example, tensile strength, elongation, tear resistance, and barrier properties are assessed to ensure the materials are suitable for their intended use.
- Compliance with Specific Regulations: Food contact materials must comply with specific regulations in each region, such as those set by the FDA in the United States or the European Commission in the EU. Compliance testing ensures that the material meets the necessary legal requirements and safety standards.
- Overall Migration Testing: This type of testing evaluates the total amount of substances migrating from the material into the food. It helps assess the overall safety of the material in contact with different types of food.
It’s essential to note that food contact material testing is a comprehensive process, and manufacturers are responsible for conducting appropriate testing to ensure the safety and compliance of their products.
It’s important to note that both the United States and the European Union have strict regulations in place to ensure the safety and suitability of food contact materials. These regulations aim to minimize the risk of chemical migration from the materials into the food and to protect public health. Manufacturers and importers of food contact materials in these regions must comply with these regulations to ensure their products meet the required safety standards.
About ACT-LAB
ACT-LAB is an ISO/IEC 17025 accredited laboratory that conducts consumer product safety and compliance testing for an active world. We can help ensure that your products both meet industry standards and are inspected to ensure the utmost quality.
To learn more about our tests contact us today.
Read more about our accreditations here.
 ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited Independent Testing Laboratory
ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited Independent Testing Laboratory